
Yuccas Around Las Vegas, Vegetation Around Las Vegas

 |
Western Joshua Tree (Yucca brevifolia), or perhaps just Yucca brevifolia, is the signature species of the Mojave Desert: if you see Joshua trees, you are in the Mojave Desert -- no questions asked. Western Joshua Trees occur to the south and west of the distribution of Joshua Trees. Eastern Joshua Trees occur in Arizona and parts of eastern California and southeastern Nevada. Link to distribution map. Western Joshua Trees differ from Eastern Joshua Trees in a number of ways, but Western Joshua Trees are taller, branch high off the ground, and have longer leaves. There are also differences in the flower, fruit, and pollinators. Joshua trees are a major component of the Upper Sonoran (Mojave Desert Scrub) life zone, and they extend into the Upper Sonoran (Pinyon-Juniper Woodland) life zone. Family: Agave (Agavaceae). Formerly Yucca brevifolia brevifolia. |
 Relatively tall in stature, first branch far from the ground |
Other Names: tree yucca, joshua tree yucca. Plant Form: Upright, many branched tree, with branches starting high off the ground. Height: To about 20-30 feet. Trunk: Generally 12-15 inches diameter, to 3 feet; brown, rough, and furrowed. Young trunks covered with dead leaves. Leaves: long (usually 8-10 inches) and narrow, straight, pointed tip, toothed margins, dark green. Live leaves clustered at the ends of branches in dense rosettes; dead leaves stay attached for years and cover the trunks. Flowers: Greenish-white, waxy, bell shaped, to 3.5 inches long. Flowers clustered on stalks (to 1.5-feet long) at the branch tips. Blooms in the spring if there have been enough cold days during winter. These flowers are short and wide compared to Eastern Joshua Tree flowers. |
 Long leaves |
Seeds: Occur in green seedpods about 1.5 inches wide and 4 inches long. These seedpods are short and wide compared to Eastern Joshua Tree seedpods. Elevation: 2,000 to 3,500 ft Comments: Joshua trees got their common name from the Mormon settlers who likened the tree to the biblical prophet Joshua with his arms uplifted towards the sky in prayer. Joshua trees can live to 300 years. Joshua Trees are pollinated by Tegeticula moths (family Prodoxidae), commonly known as Yucca Moths. Western Joshua Trees are pollinated by Western Joshua Tree Moths (Tegeticula synthetica). |
 Short, fat seedpods |
Many species of wildlife use Joshua trees. In places where Joshua trees are the only "trees" around, woodpeckers drill nest holes into the trunks, holes that are then used by other nesting birds in later years. Desert Night Lizards depend entirely on Joshua trees and other yuccas, living only under the bark and in the dead trunks of these species. Desert Woodrats often nest in the hollow trunks of dead Joshua trees. During drought and other times of stress, Desert Woodrats sometimes chew off the leaves of Joshua Trees. Sometimes the cut leaves are left on the ground, other times they seem to have been chewed or eaten, and sometimes they are used to armor the Woodrat's nest. |
 Relatively tall in stature, first branch far from the ground |
 Relatively tall in stature, first branch far from the ground |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 This one looks a bit confused |
 Long leaves |
 Long leaves |
 Long leaves |
 |
 |
 Short, fat seedpods |
 Short, fat seedpods, and a Gambel's Quail |
 Joshua tree flower cluster |
 Joshua tree flower cluster |
 Joshua tree flower |
 Joshua tree flower |
 Joshua tree flower |
 Joshua tree flower |
 Joshua tree flower petal and stamen |
 Joshua tree flower with petals removed |
 Joshua tree ovary cross-section |
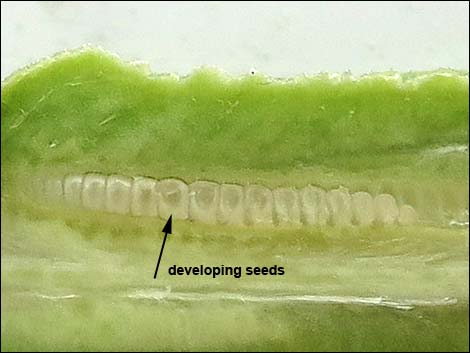 Cross-section of Joshua tree ovary with developing seeds |
Note: All distances, elevations, and other facts are approximate. Names generally follow the USDA database.
![]() ; Last updated 241226
; Last updated 241226
| All Yuccas | Plant Species Index | Glossary | Copyright, Conditions, Disclaimer | Home |